Here is an example to illustrate the comparison of these three calculation methods, stones are rolled down from the top of a hill, and we are to estimate where they will hit the wall. Due to the uncertainty of the shape of the stones and the nonuniform surface roughness, this problem is difficult to solve in a theoretical way. Moreover, the collision position is not truly random, and errors may be introduced by statistical theory.
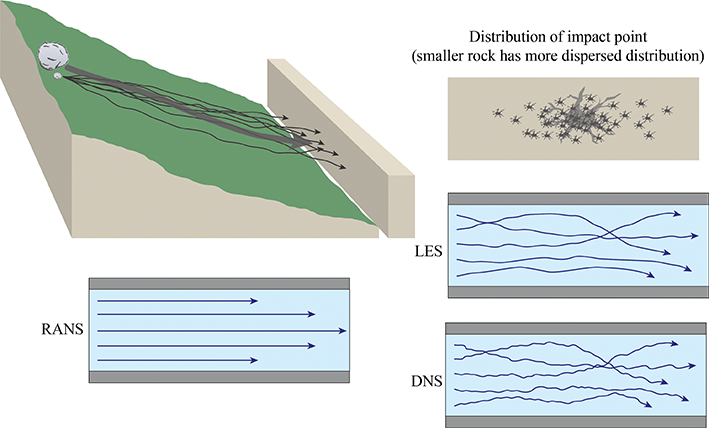
Since DNS takes all details of a flow field into account, the solutions are greatly affected by small perturbations, resulting in a large dispersion of the solutions. One needs to average the time-dependent values to obtain the averaged solution Since RANS ignores the details and impacts of small turbulent fluctuations, the solution might be closer to the average result. So, the RANS approach appears to be sufficient if one is interested only in the averaged flow However, there is no perfect turbulence model to simulate the effect of the small-scale turbulence on the average flow. Therefore, there is no guarantee that the RANS results will reproduce the averaged DNS results
In general, the time-averaged flow field obtained using DNS or LES should be more accurate. In conclusion, RANS yields the averaged flow field just in theory, while DNS and LES are able to provide more details of the flow field. For the majority of engineering problems, the most important result should be an accurate time-averaged flow field. RANS will be the major method for a rather long period of time
1Hongwei Wang (2023). A Guide to Fluid Mechanics. National Defense Industry Press.