Turbulence Modeling
Time-averaging approach:
need to solve the closure problem for the Reynolds stresses, such as $-\rho \overline{u'v'}$, etc
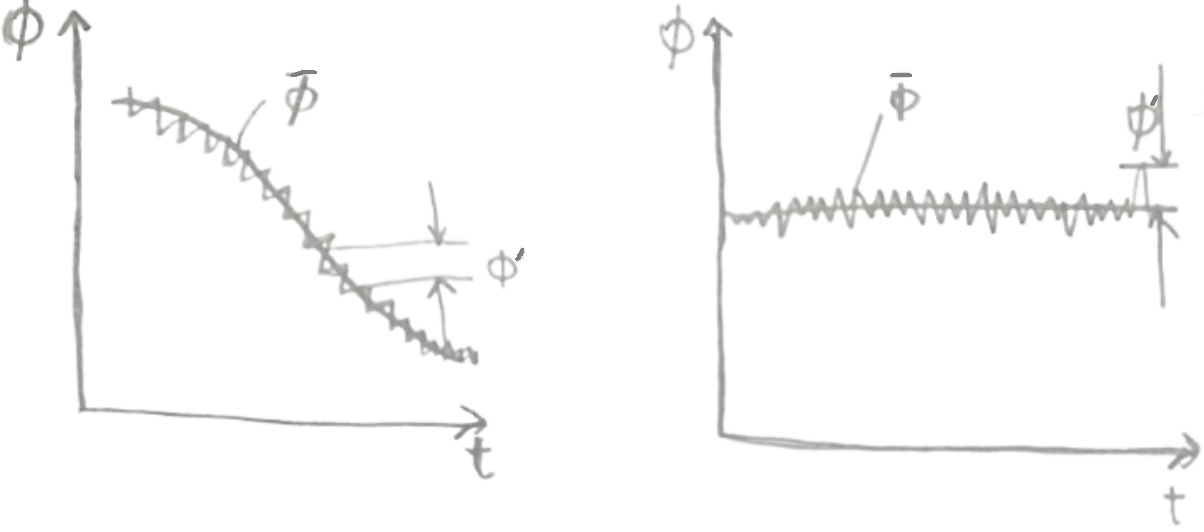
In the Reynolds averaging method, the time interval $\Delta t$ for averaging any variable must satisfy certain requirements. Relative to the random fluctuation period of turbulence, $\Delta t$ must be sufficiently large; relative to the slow variation of the mean flow field, $\Delta t$ must be sufficiently small (see the definition of continuum)
Different methods for Reynolds stress closure
- Algebraic (zero-equation) models — by modeling the eddy viscosity or mixing length
- One-equation models — solve one additional transport equation
- Two-equation models — solve two more additional transport equations, such as $k$-$\varepsilon$ model, $k$-$\omega$ model
- Reynolds stress transport models — solve the transport equation for Reynolds stresses
Large eddy simulations (LES) — explicitly solve for the large eddies in a calculation and implicitly
account for the small eddies by using a subgrid-scale model (SGS model)
Direct numerical simulations (DNS) — directly solve the transient 3D Navier-Stokes equations with very fine grids and time steps
1National Tsing Hua University OpenCourseWare(NTHU, OCW). Fluid Mechanics. WONG, SHWIN-CHUNG. Chapter 8: Viscous Flow in Pipes.