| Physics | Dirichlet | Neumann | Robin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid Mechanics | Displacement | Traction (stress) | Spring |
| Heat Transfer | Temperature | Heat flux | Convection |
| Pressure Acoustics | Acoustic pressure | Normal acceleration | Impedance |
| Electric Currents | Fixed potential | Fixed current | Impedance |
The Periodic or Cyclic boundary condition defines a cyclic/repeating situation of the flow across the boundary surface. Tt is mandatory to select two boundary faces that will be treated as if they are physically connected. The flow exiting/entering from one face then enters/exits the other face (ocean!)
\(\text{No-Slip Wall Boundary} \left(p_b = ?;\, \dot{m}_b = 0;\, \mathbf{v}_b = \mathbf{v}_{\text{wall}}\right)\)
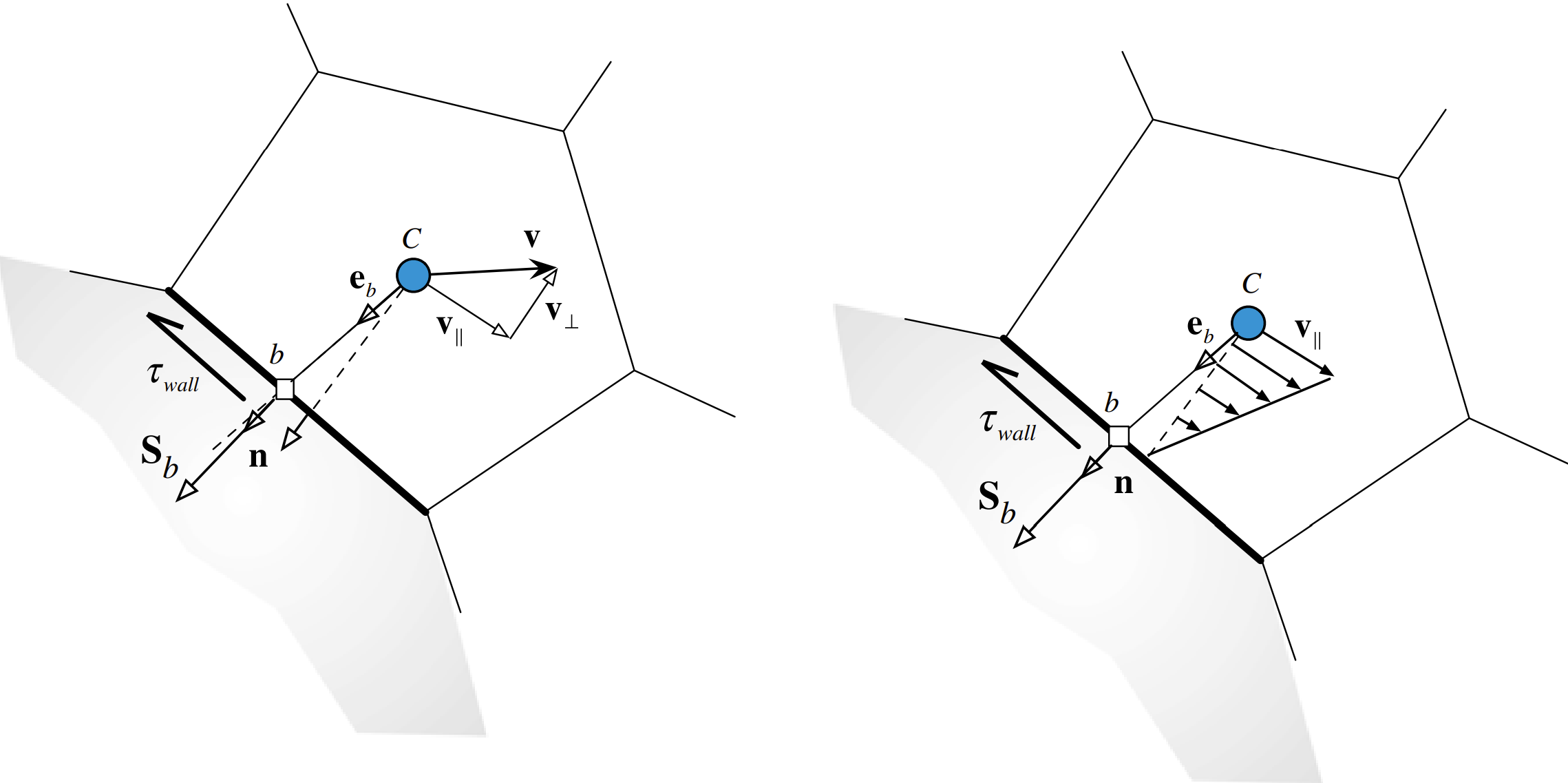
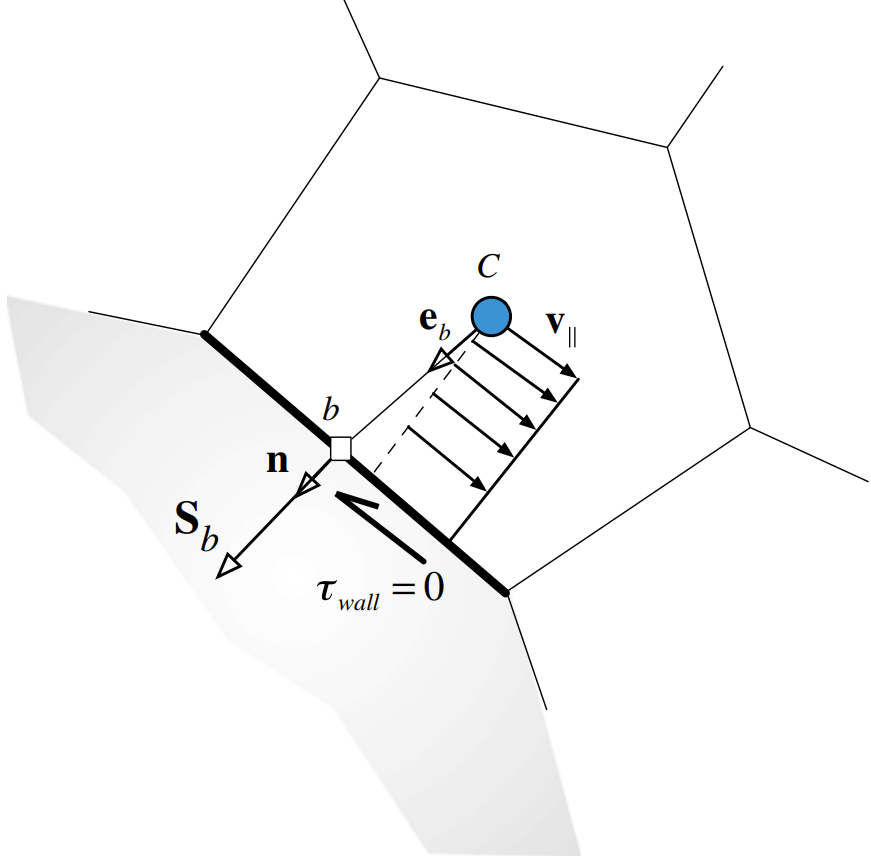
\(\text{Slip Wall Boundary} \left(p_b = ?;\, \dot{m}_b = 0;\, \mathbf{F}_b = 0\right)\)
1 Henrik Sönnerlind. (2016). How to Make Boundary Conditions Conditional in Your Simulation. COMSOL Blog
2 F. Moukalled, L. Mangani, M. Darwish. (2015). The Finite Volume Method in Computational Fluid Dynamics: An Advanced Introduction with OpenFOAM® and Matlab. Springer Cham.