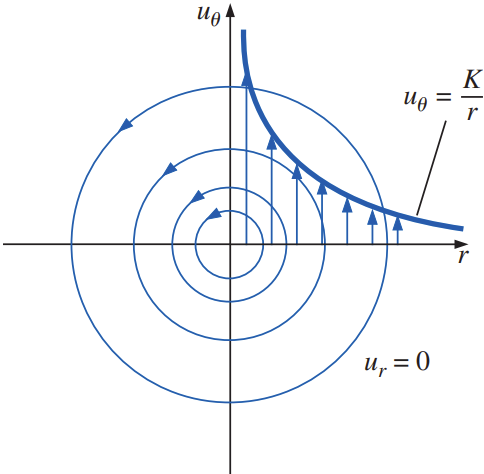
[Ex] Consider a steady, two-dimensional, incompressible velocity field expressed in cylindrical coordinates \((r,\theta,z)\), with the axis aligned along the \(z\)-direction. The velocity components are given by
\[
u_r = 0, \qquad
u_\theta = \frac{K}{r},
\]
where \(K\) is a constant.
Assume that the flow is independent of \(z\) and that body forces are negligible. Determine the pressure field \(p(r,\theta)\) associated with this flow.
 ◀
▶
◀
▶