Drag and Losses
Drag and losses are the eternal problems of fluid mechanics in engineering applications. There is still no general agreement about how to solve the problems related to flow drag and losses. At present, we can only solve specific problems through special analysis, but the accuracy of simulation results cannot be guaranteed. In most cases, we still rely on the data obtained from experiments and empirical models
As inviscid fluid produces no flow drag or losses. Therefore, it is necessary to study the working mechanism of viscosity in order to calculate the flow drag or losses.
This problem can become exceedingly complicated in turbulent flow, which is characterized by the enhanced viscous shear force and dissipation.
So far, the extra viscosity in turbulent flow, known as eddy viscosity, cannot be properly estimated, which is the bottleneck to a better estimation of drag or losses
In engineering, the flow drag due to the differential pressure between windward side and leeward side surfaces of an object is called pressure drag or shape drag. Although completely created by differential pressure force, the pressure drag is not meant to be independent of viscous force.
The drag due to viscous shear stresses acting on the lateral surface of an object is called frictional drag
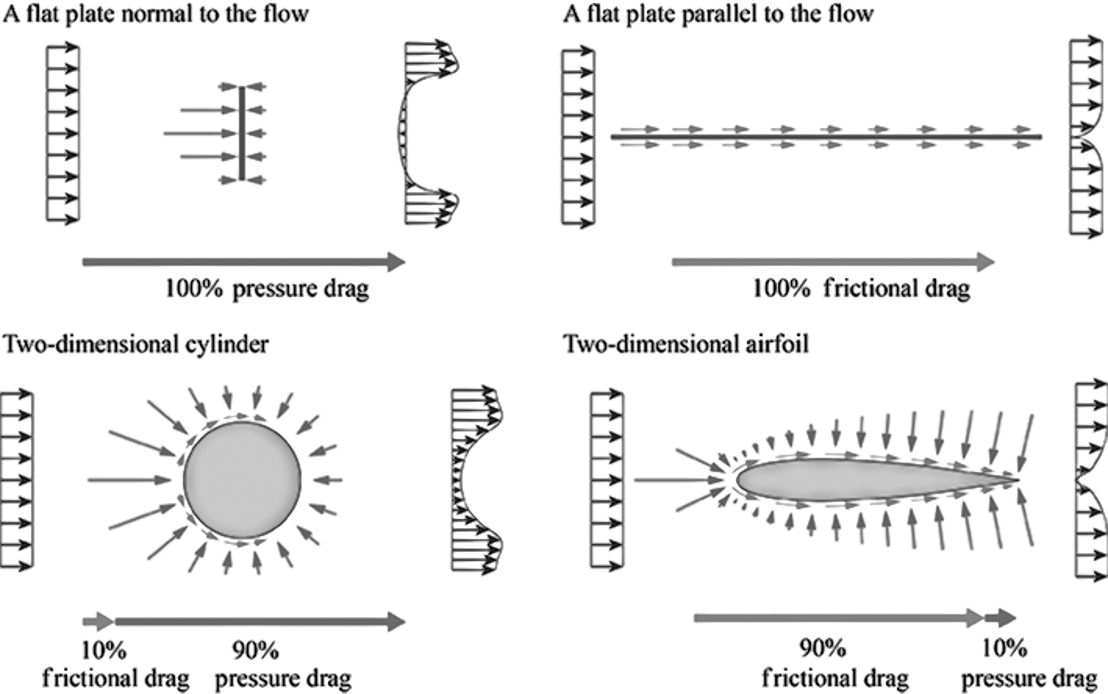
The ratios of pressure drag and frictional drag to total drag for several typical objects.
1Hongwei Wang (2023). A Guide to Fluid Mechanics. National Defense Industry Press.