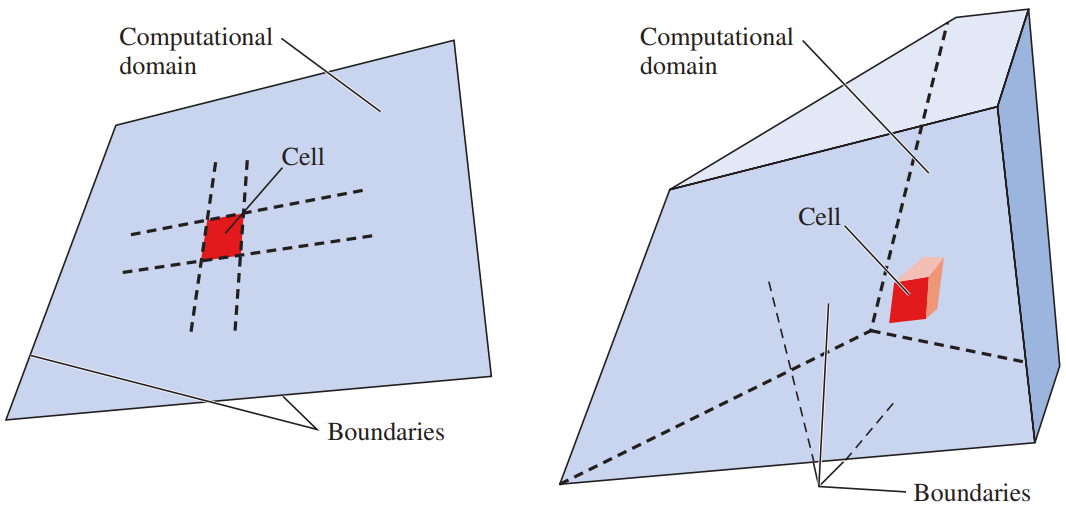
The domain is divided into many small elements called cells. For two-dimensional (2-D) domains the cells are areas, while for three-dimensional (3-D) domains the cells are volumes. You can think of each cell as a tiny control volume in which discretized versions of the conservation equations are solved.
A computational domain is the region in space in which the equations of motion are solved by CFD. A cell is a small subset of the computational domain. The boundaries of a 2-D domain are called edges, while those of a 3-D domain are called faces.
The quality of a CFD solution is highly dependent on the quality of the grid. Therefore, you are advised to make sure that your grid is of high quality before proceeding to the next step. Do not proceed with CFD calculations until you have generated a high-quality grid.
1Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications Fourth Edition. Çengel and J. M. Cimbala, McGraw-Hill, New York (2018)