Internal Waves
Sometimes the internal waves break and generate smaller-scale turbulence in a somewhat similar manner to bubble and foam generation by breaking surface waves.
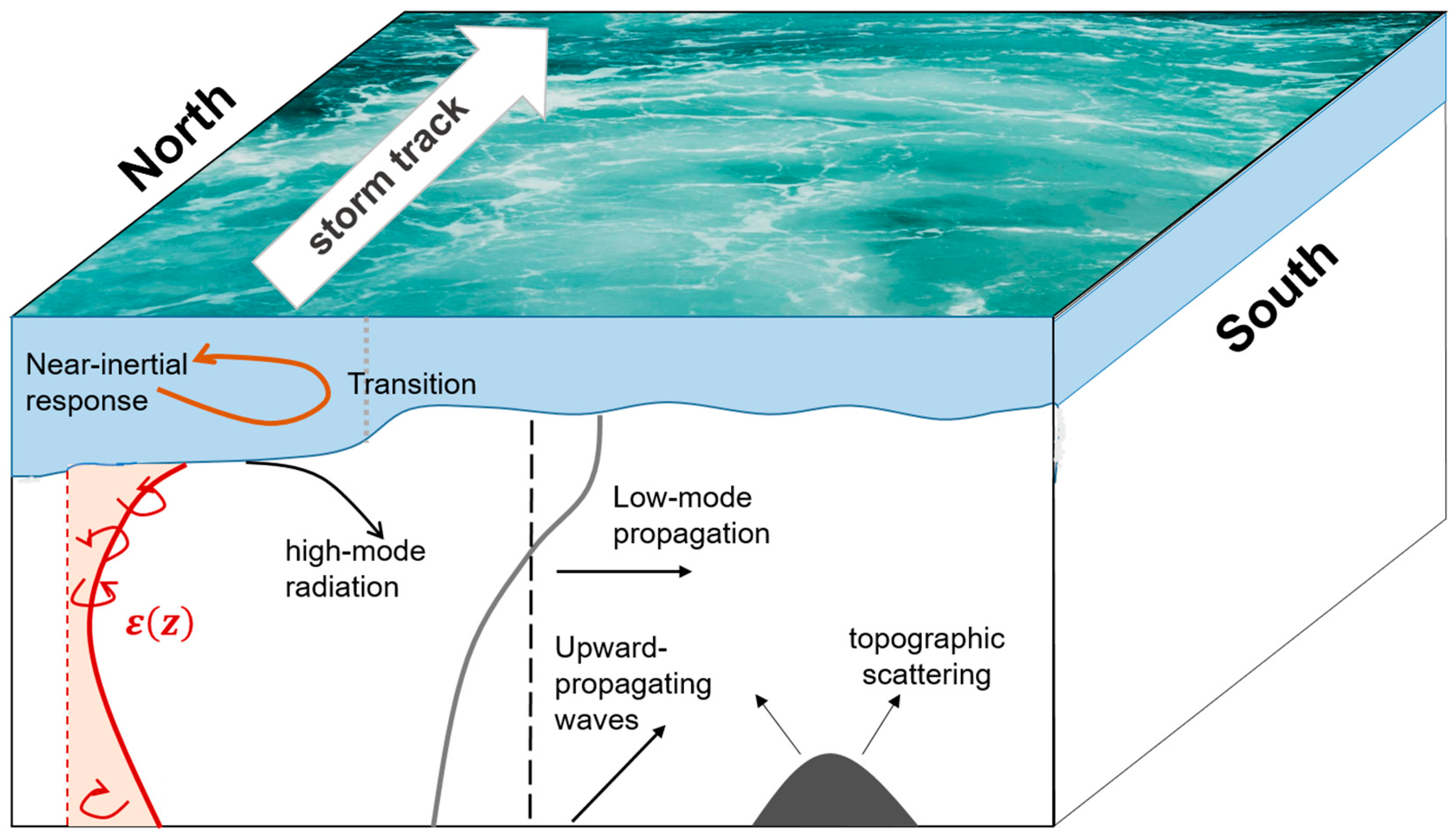
Schematic showing processes associated with near-inertial generation, dissipation, and propagation. Such internal waves are often generated by storms at sea. Their wave propagation direction tends to be vertical, while the oscillation direction tends to be horizontal. They contain about half of the total energy in the internal wave spectrum and are associated with strong vertical shear. They play an important role in maintaining ocean stratification, as well as in the transport of matter and energy.
1Li Y, Xu Z, Lv X. The Generation and Propagation of Wind- and Tide-Induced Near-Inertial Waves in the Ocean. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(9):1565. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12091565