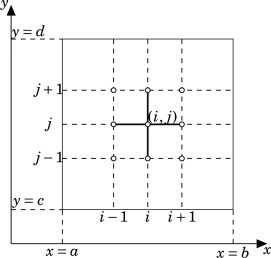
Laplace and Poisson equations are elliptic partial differential equations and occur in many practical situations such as inviscid flow (also called potential flow or ideal fluid flow), heat conduction, mass diffusion etc. These equations are boundary value problems applied over multi-dimensions.
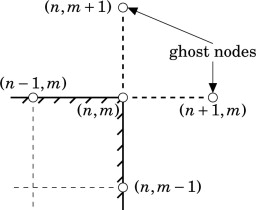
The corner node may be associated partly to the plane parallel to the y axis and partly to the plane parallel to the x axis. We may assume that the Robin condition is the mean of the two. Ghost nodes are used to simplify the implementation of boundary conditions at corners by introducing additional points that allow for a more accurate numerical approximation of mixed or Robin conditions.
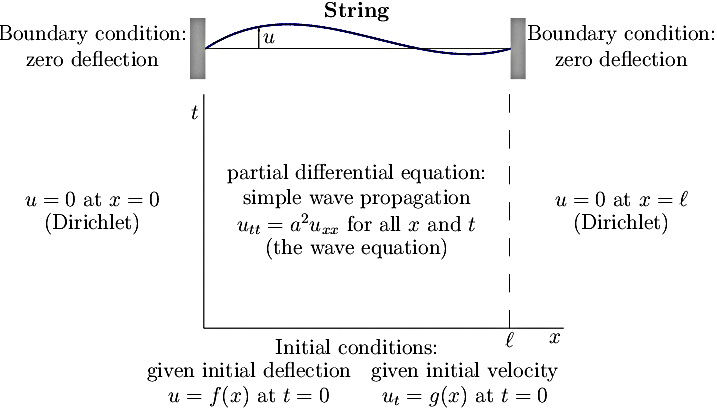
The wave equation typically requires initial-value or initial/boundary-value problems. Unlike the heat equation, which needs only one initial condition, the wave equation, being second order in time, requires two initial conditions:
- the initial transverse displacement \( u(x,0) \)
- the initial transverse velocity \( u_t(x,0) \)