Motion of a Fluid Particle (Kinematics)
The following text should help wrap up different modes of fluid motion and deformation
- Translation: This is controlled by the acceleration. Specially, for steady flow, the convective acceleration will play the main role. For each component of the acceleration (e.g. \(x\)-component) this is the dot product of the velocity field with the gradient, that acts on the same component of the velocity (\(x\)-component)
- Rotation: This measures the spinning motion of fluid particles in any flow, and is simply found by taking the curl of the velocity field
- Dilation/Compression: This measures how much a fluid element expands or shrinks due to sources or sinks in the flow, and is the divergence of the velocity field
- Angular deformation: This is a measure of shear-like deformations in the flow, and is found by summing the cross gradients of each component of the velocity field, i.e. in the \(x – y\) plane summing \( \partial_y v_x \) and \( \partial_x v_y \)
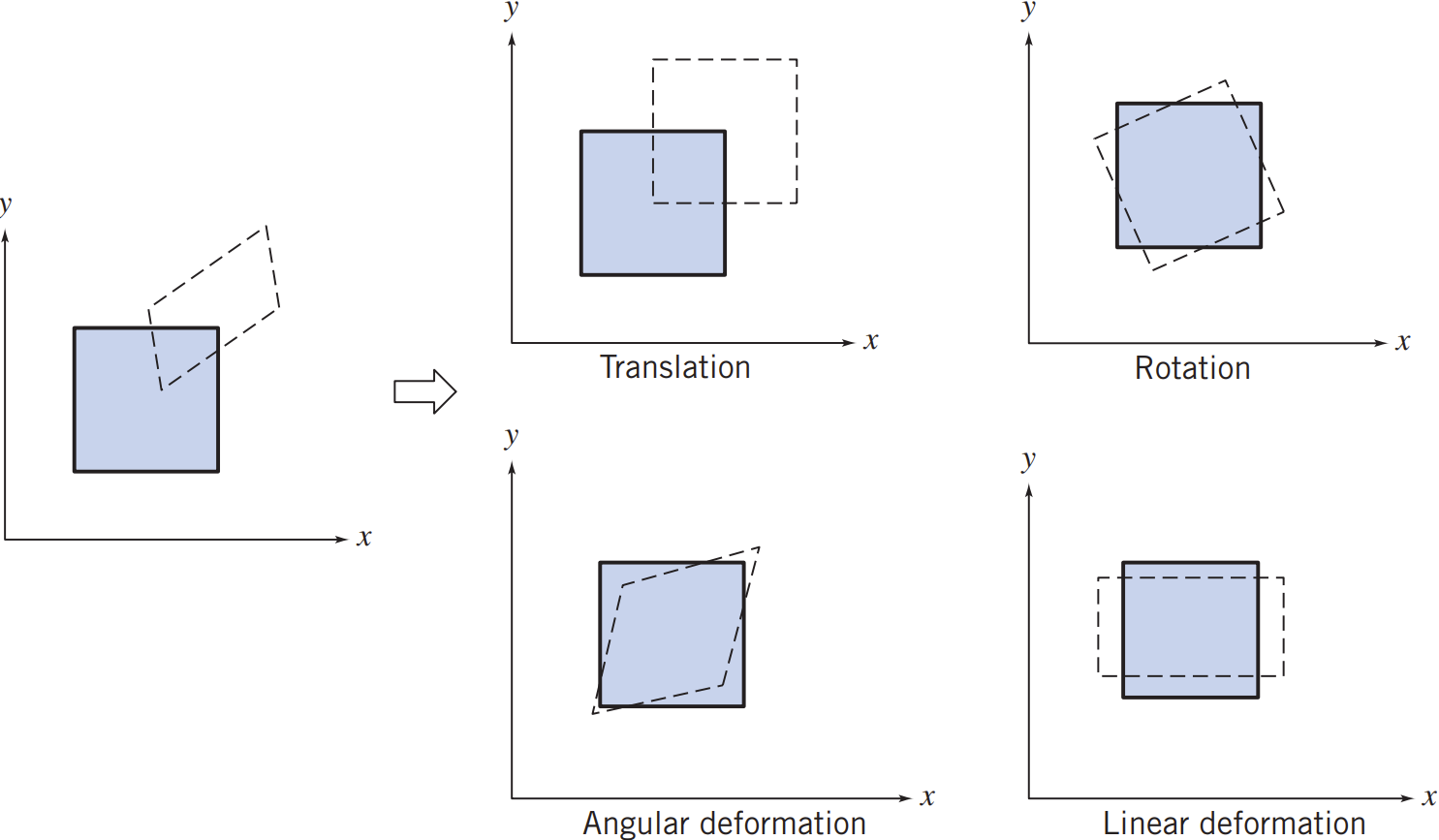
Pictorial representation of the components of fluid motion